Macromolecules
PULSE PROGRAMS
Dynamic NOE measurements: a tool for studying protein dynamics


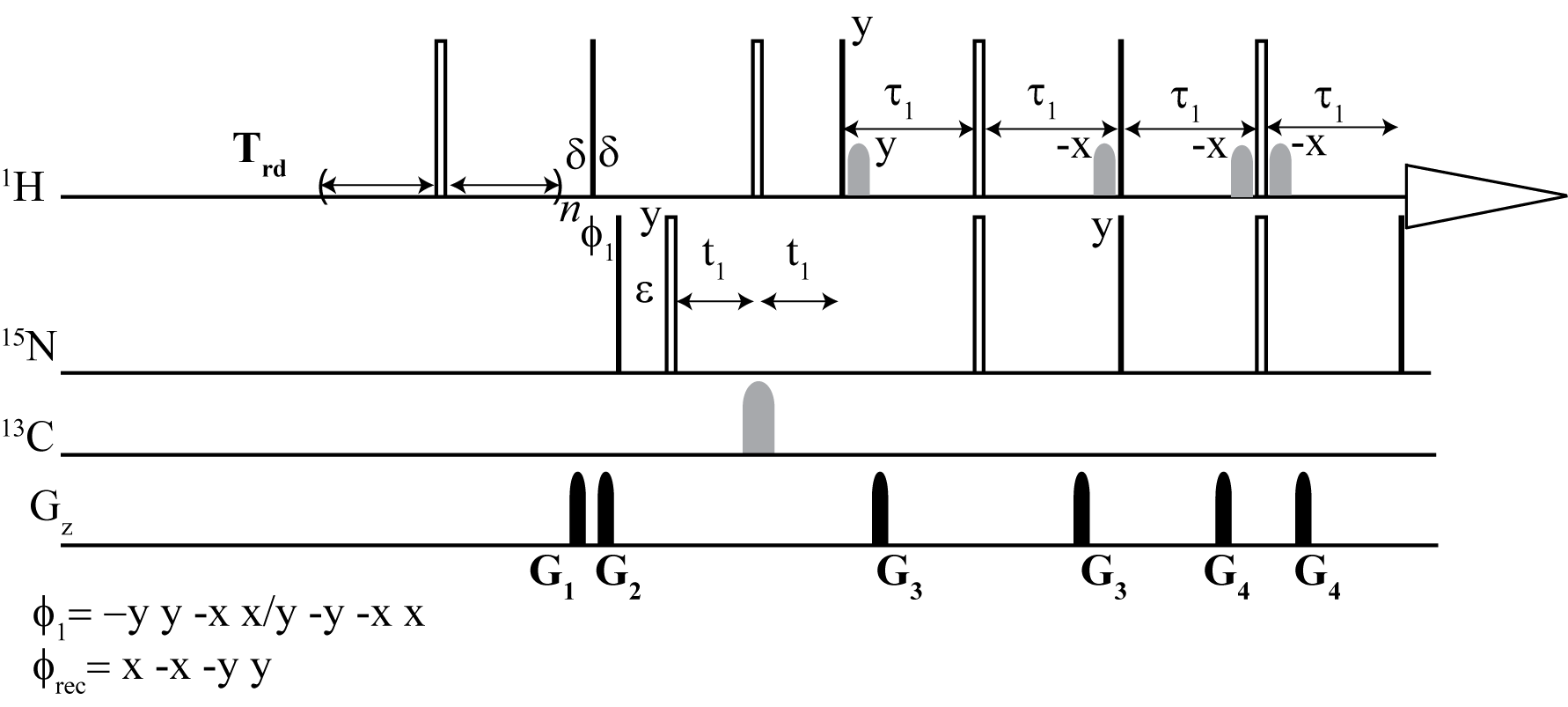
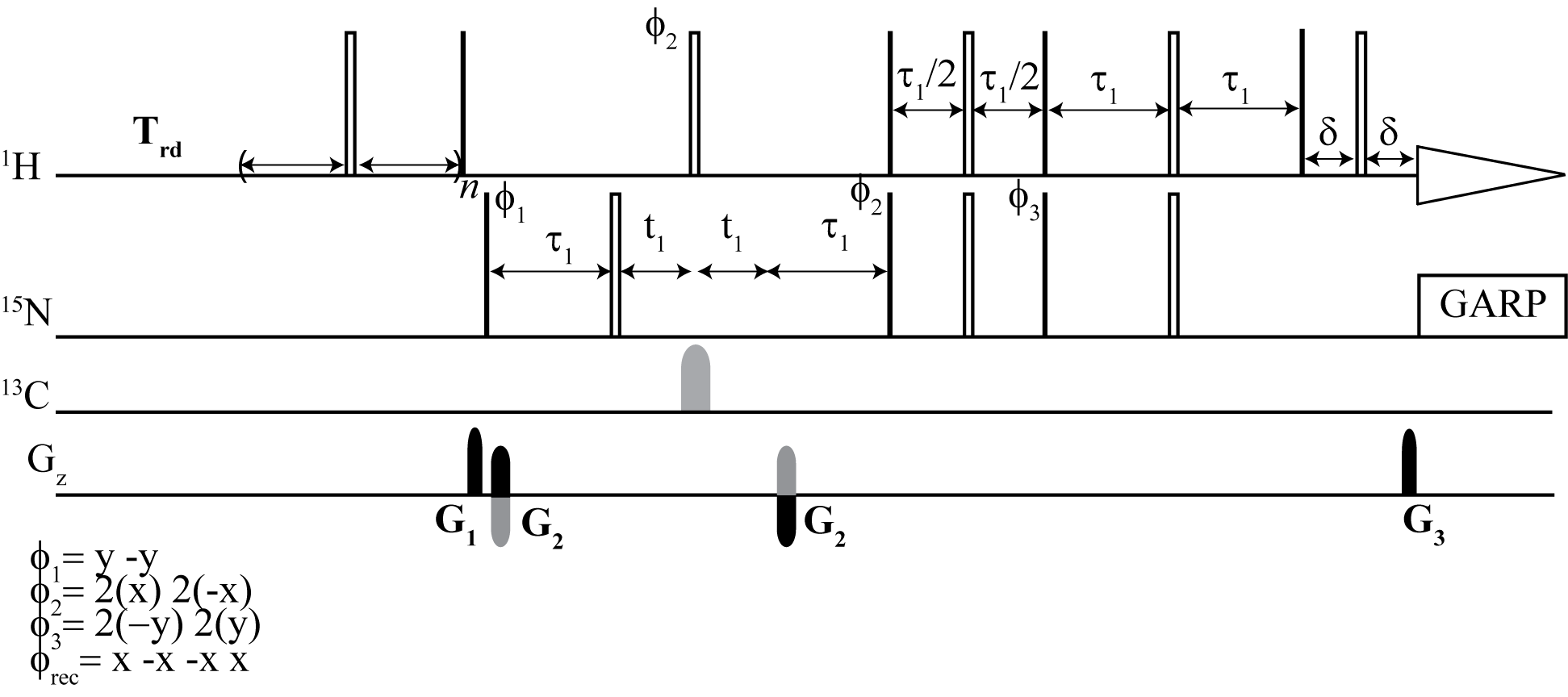
From the top: Dynamic NOE 2D 1H -15N TROESY, Dynamic NOE 2D 1H - 15N HSQC
We have developed an alternative method to steady-state NOE measurements for proteins that provides a robust and more accurate alternative.
Here, we have shown that dynamic NOE measurement is an efficient and accurate method for NOE determination. In particular, it presents its usefulness in cases of NOE values that are close to zero. This method provides a robust and more accurate alternative to widely used steady-state NOE measurement. The DNOE measurement allows for the determination of NOE values and their accuracies with standard nonlinear regression methods. If high accuracy longitudinal relaxation rates R1 are not of great importance, they can be simultaneously obtained with a reduced accuracy as a "by-product" in the DNOE.
COMPUTATIONAL TOOLS
Fast evaluation of protein dynamics from deficient 15N relaxation data
Three methods of analysis of limited relaxation data have been independently developed. One of them is based on the observation that one of the model free approach parameters, the generalized order parameter, S2, can be extracted with a reasonable accuracy from a linear combination of relaxation rates, 2R2 − R1. Another method investigates the product of relaxation rates R1R2 also giving access to the S2 parameter. The last method of the S2 parameter extraction from R1 and R2, measured with the CEST technique to save experimental time and named lean MFA (LMFA), relies on the least squares minimization spatial freedom of motion.
Our group has conducted comparative analysis of three mentioned above combinations of relaxation rates, which allows to select the optimal method of the MFA parameter elucidation from deficient relaxation data. The utility of this approach is presented by applying it to the relaxation data of four proteins of different size: immunoglobulin-binding domain of streptococcal protein G, GB1, human ubiquitin , human S100A1 calcium binding protein in apo state, and β-lactamase PSE-4.